Decentralized Applications
As opposed to centralized applications that run on a single computer, decentralized applications run on a P2P network of computers. They have existed since the advent of P2P networks.
Decentralized applications don‘t necessarily need to run on top of a blockchain network. Tor, BitTorrent, Popcorn Time, BitMessage, are examples for decentralized applications that run on a P2P network, but not on a blockchain – which is a special kind of P2P network (read more: Origins of Bitcoin and Web3).
Decentralized applications are a piece of so ware that communicates with the blockchain, which manages the state of all network actors. The interface of the decentralized applications does not look any different than any website or mobile app today. The smart contract represents the core logic of a decentralized application. Smart contracts are integral building blocks of blockchains, that process information from external sensors or events and help the blockchain manage the state of all network actors.

The frontend of a decentralized application represents what you see, and the backend represents the entire business logic. This business logic is represented by one or several smart contracts interacting with the underlying blockchain. The frontend, as well as files like a photo, a video, or audio, could be hosted on decentralized storage networks such as Swarm or IPFS. Traditional Web applications use HTML, CSS, and javascript or the like to render a webpage. This page interacts with a centralized database, where all the data is stored. When you use a service like Twitter, Facebook, Amazon, or Airbnb, for example, the webpage will call an API to process your personal data and other necessary information stored on their servers, to display them on the page. User ID and passwords are used for identification and authentication, with low levels of security, since personalized data is stored on the server of the service provider.
Traditional websites: Front End → API → Database.
Decentralized applications are similar to a traditional Web application. The frontend uses the exact same technology to render the page. It contains a “wallet” that communicates with the blockchain. The wallet manages cryptographic keys and the blockchain address. Public-key infrastructure is used for user identification and authentication. Instead of an API connecting to a database, a wallet so – ware triggers activities of a smart contract, which interacts with a blockchain:
Web3 compatible website:
Front End (including wallet) → Smart Contract → Blockchain.
In contrast to Web2 applications, Web3 applications need a connection to the blockchain, which is managed by a special application called “wallet.” It keeps a record of the private keys and blockchain address, which represents the unique 30 identities and point of reference. Without a so ware that manages our digital identity, we will not be able to interact with the blockchain. The Web3, therefore, builds on the current Web2 stack and introduces additional elements on an application level. In the backend, the Web3 adds a whole new infrastructure layer for decentralized applications to interact with – the decentralized protocol stack. Decentralized apps need to have a component that manages a user’s private keys, with which one can sign transactions on the state layer, the blockchain (read more: Token Security – Cryptography).
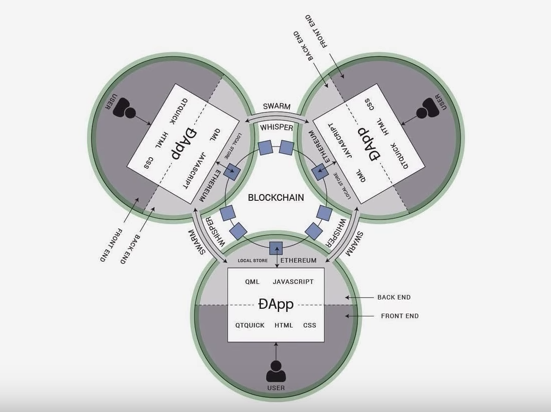
Illustration of a DApp that uses a blockchain with smart contracts combined with the pillars of Swarm and Whisper.
Source: Ethereum Stack exchange
Trending Technologies 2020
What are the two main ways to store a document on the blockchain
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have shown the use of blockchain technology for different forms of money and currency. Although they store transactions within blocks, we can no doubt extend this data beyond financial data. In theory, we can store any form of data on...
Notary Public: 5 Tips to Increase Productivity
A notary public's job is a complex one. The work involves witnessing and taking care of relevant documents. As there is much paperwork required in this job, taking care of everything can be a little overwhelming. This is where blockchain comes into the picture....
Why do you need MetaMask?
MetaMask is a cryptocurrency wallet that allows you to interact with the Ethereum enabled distributed applications(Dapps) without having the need to run the Ethereum node. It is available as a browser extension that allows smooth interaction between the web...
SAFEBOX Pricing
SAFEBOX makes use of cloud storage and blockchain technology to facilitate the work related to records. Our platform takes care of signing agents, attorneys, medical professionals, title companies, automobile dealers, escrow companies, and many more who need to store...
5 Ways Blockchain technology is transforming the signing agent’s work
The blockchain's primary features have proved to be a great asset in improving the signing agent capabilities. With the help of blockchain technology, a signing agent can do most of the work remotely. Blockchain technology has transformed the signing agent's work in...
Our Latest Updates

Security Issues with Document Sharing Technologies
Today, the corporate world is undergoing a swift change in operations, a feat that has been greatly influenced by technological advances. Employees are using different techniques to transfer important documents to clients and fellow workers. This has revolutionized...
How Can Blockchain Technology Improve Data Storage?
Decentralized Cloud Storage Cloud storage systems maintain data on remote servers that are accessible from the internet. However, unlike conventional cloud servers, decentralized cloud storage does not keep user data on a single centralized server. A decentralized...
What are the two main ways to store a document on the blockchain
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have shown the use of blockchain technology for different forms of money and currency. Although they store transactions within blocks, we can no doubt extend this data beyond financial data. In theory, we can store any form of data on...